Page 83 - MBCA_FULL REPORT_FINAL_FOR_WEB
P. 83
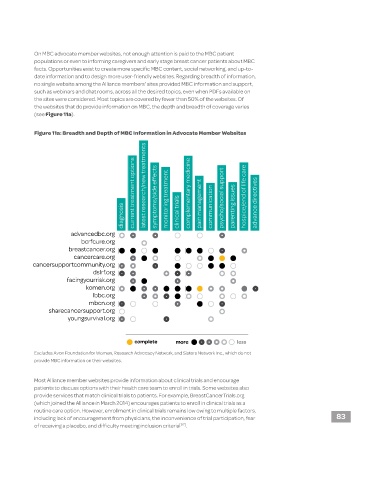
On MBC advocate member websites, not enough attention is paid to the MBC patient
populations or even to informing caregivers and early stage breast cancer patients about MBC
facts. Opportunities exist to create more specific MBC content, social networking, and up-to-
date information and to design more user-friendly websites. Regarding breadth of information,
no single website among the Alliance members’ sites provided MBC information and support,
such as webinars and chat rooms, across all the desired topics, even when PDFs available on
the sites were considered. Most topics are covered by fewer than 50% of the websites. Of
the websites that do provide information on MBC, the depth and breadth of coverage varies
(see Figure 11a).
Figure 11a: Breadth and Depth of MBC Information in Advocate Member Websites
current treatment options latest research/new treatments symptoms/side effects monitoring treatment complementary medicine pain management psycho/social support hospice/end of life care advance directives
diagnosis clinical trials communication parenting issues
advancedbc.org
bcrfcure.org
breastcancer.org
cancercare.org
cancersupportcommunity.org
dslrf.org
facingyourrisk.org
komen.org
lbbc.org
mbcn.org
sharecancersupport.org
youngsurvival.org
complete more less
Excludes Avon Foundation for Women, Research Advocacy Network, and Sisters Network Inc., which do not
provide MBC information on their websites.
Most Alliance member websites provide information about clinical trials and encourage
patients to discuss options with their health care team to enroll in trials. Some websites also
provide services that match clinical trials to patients. For example, BreastCancerTrials.org
(which joined the Alliance in March 2014) encourages patients to enroll in clinical trials as a
routine care option. However, enrollment in clinical trials remains low owing to multiple factors,
including lack of encouragement from physicians, the inconvenience of trial participation, fear 83
of receiving a placebo, and difficulty meeting inclusion criteria [97] .